Intercepts of a Line
Each of the points at which a line crosses the
x-axis and the
y-axis is called an intercept of the line.
x-intercept and y-intercept of a line
The
x-intercept is the point,
(a,0), where the graph crosses the
x-axis. The
x-intercept occurs when
y is zero.
The
y-intercept is the point,
(0,b), where the graph crosses the
y-axis. The
y-intercept occurs when
x is zero.
example
Find the intercepts of
2x+y=6
We'll fill in the table below.
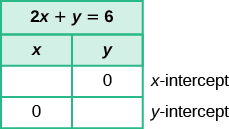
To find the x- intercept, let
y=0 :
|
2x+y=6 |
| Substitute 0 for y. |
2x+0=6 |
| Add. |
2x=6 |
| Divide by 2. |
x=3 |
| The x-intercept is (3,0). |
|
To find the y- intercept, let
x=0 :
|
2x+y=6 |
| Substitute 0 for x. |
2⋅0+y=6 |
| Multiply. |
0+y=6 |
| Add. |
y=6 |
| The y-intercept is (0,6). |
|
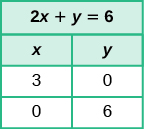
The intercepts are the points
(3,0) and
(0,6) .
example
Find the intercepts of
4x−3y=12
Answer:
Solution
To find the x-intercept, let y=0.
|
4x−3y=12 |
| Substitute 0 for y. |
4x−3⋅0=12 |
| Multiply. |
4x−0=12 |
| Subtract. |
4x=12 |
| Divide by 4. |
x=3 |
The
x-intercept is
(3,0).
To find the
y-intercept, let
x=0.
|
4x−3y=12 |
| Substitute 0 for x. |
4⋅0−3y=12 |
| Multiply. |
0−3y=12 |
| Simplify. |
−3y=12 |
| Divide by −3. |
y=−4 |
The
y-intercept is
(0,−4).
The intercepts are the points
(−3,0) and
(0,−4).
| 4x−3y=12 |
| x |
y |
| 3 |
0 |
| 0 |
−4 |
Did you have an idea for improving this content? We’d love your input.
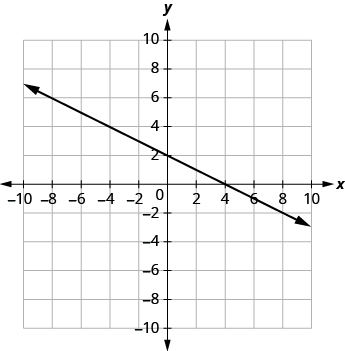
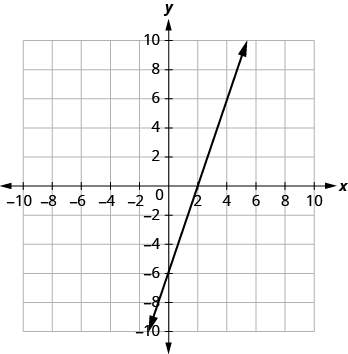
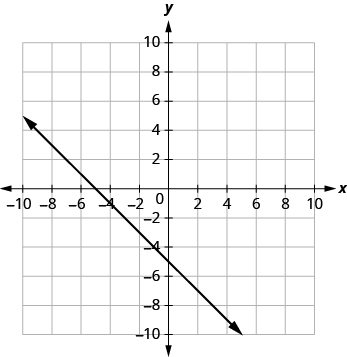
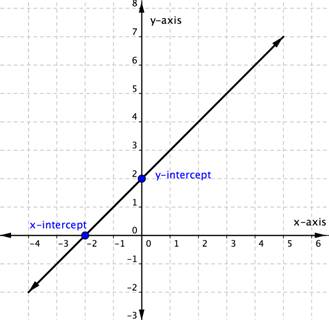 In the graph above, the x-intercept occurs when and the y-intercept occurs when . We typically express the intercepts by giving the ordered pair, so we say that the x-intercept above is at the point and the y-intercept above is at the point .
Notice that the intercept always occurs where , and the x-intercept always occurs where .
Let’s look at the graph of the lines shown below.
In the graph above, the x-intercept occurs when and the y-intercept occurs when . We typically express the intercepts by giving the ordered pair, so we say that the x-intercept above is at the point and the y-intercept above is at the point .
Notice that the intercept always occurs where , and the x-intercept always occurs where .
Let’s look at the graph of the lines shown below.
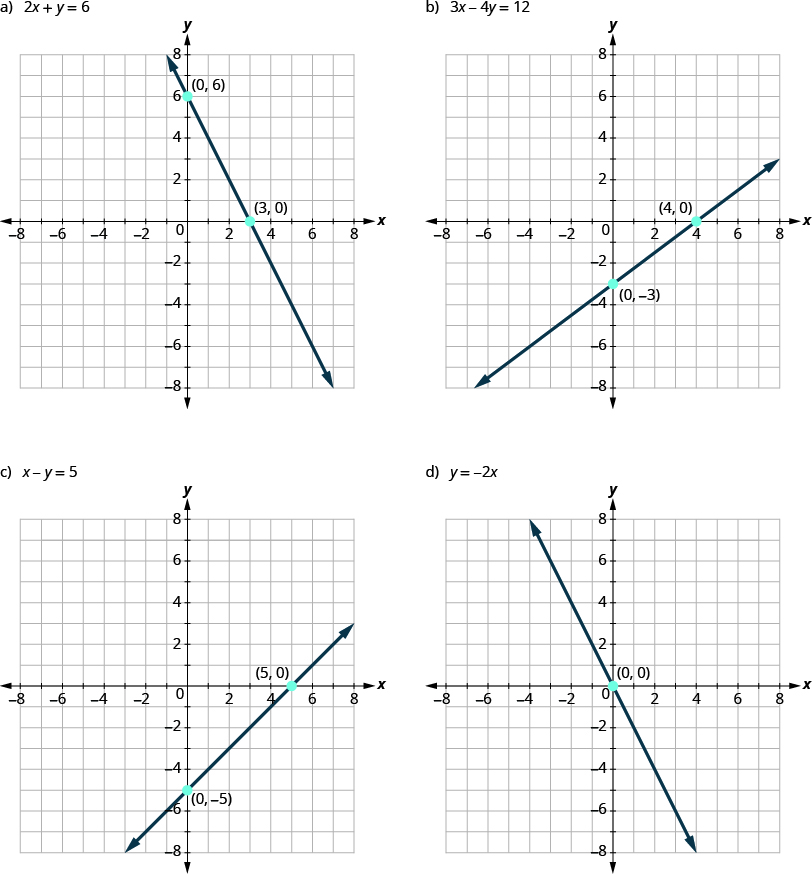 First, notice where each of these lines crosses the x- axis:
First, notice where each of these lines crosses the x- axis:
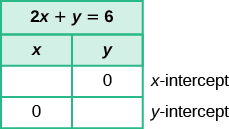 To find the x- intercept, let :
To find the x- intercept, let :
 The intercepts are the points and .
The intercepts are the points and .
